WHAT IS YOUR BODY TYPE?
Before going to start your training and nutrition regimen, it’s important for you to understand what is your body type? The three basic human body types are the endomorph, the mesomorph, and the ectomorph. Knowing your body type will be going to help you in the long run. You can acquire the correct workout plan and diet plan for your body type, and by doing so you’ll be going to set your realistic and attainable goals.
Is it an ectomorph, mesomorph or endomorph?
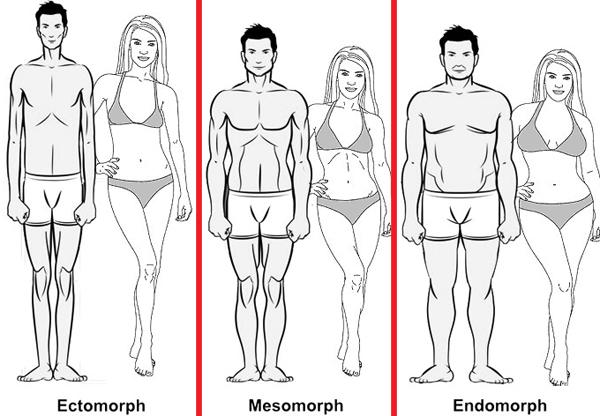
ECTOMORPH
Mesomorph
Mesomorph is the most desired body type and can also be said as ‘genetically gifted’ body. They naturally have a lean, compact and strong body.
SOME TRAITS OF MESOMORPH:
- Muscular body
- Naturally lean
- Strong body type
- Shoulders are wider than hips
- Gain muscles easily
- Natural born athletic body
Endomorph
Endomorph can easily be figured out due to their body type. Endomorphs have a naturally chubby, round and soft physique. They have wide bone structure also have a high level of body fat. Endomorphs have a high amount of fat in their body as compared to muscles.
SOME TRAITS OF AN ENDOMORPH:
- Chubby body
- Round and soft physique
- Wide bone structure
- High level of body fat
- High fat-to-muscle ratio
- Gain weight easily
- Difficulty in losing weight
According to your ectomorph, endomorph or mesomorph body type, your training program should be arranged according to the diet program you have planned. In other words, create a calorie surplus in a weight-gain training program, or create a calorie deficit in a weight-loss training program and lose weight.
BODYBUILDING – STRATEGY
In order to achieve muscle growth (hypertrophy), bodybuilders focus in three main lines of action:
- Weight training
- Nutrition
- Adequate rest
HOW MUCH WEIGHT SHOULD I LIFT TO GAIN MUSCLE?
For hypertrophy, 3 to 6 sets of 6 to 12 repetitions per exercise with a moderate load (60% to 85% of one-rep max) is ideal. More advanced individuals looking to further develop muscle mass can perform 3 to 6 sets of 8 to 12 repetitions at 70% to 85% of one-rep max.
Beginners are advised to start with light weights and focus on proper technique. Building a strong foundation and gradually progressing in weight and intensity will help you safely and effectively achieve your muscle gain goals.
HOW MANY SETS AND REPS SHOULD I DO?
Different training organizations, such as the American Council on Exercise (ACE) or the National Academy of Sports Medicine (NASM), have slightly different models for each training goal. But they follow the same general guidelines.
| Training Goal | Sets | Reps | Rest Period | Intensity / Weight |
| General fitness | 1-3 | 12-15 | 30 to 90 seconds | Varies |
| Endurance | 2-4 | 12-20 | Up to 30 seconds | <67% of 1RM |
| Hypertrophy | 3-6 | 6-12 | 30 to 90 seconds | 60% to 85% of 1RM |
| Muscle strength | 2-6 | <6 | 2 to 5 minutes | >85% of 1RM |
| Power: Single rep | 3-5 | 1-2 | 2 to 5 minutes | 80%–90% of 1RM |
| Muscle Power | 3-6 | 1-3 | 2 to 5 minutes | 30%–60% of RM |
RECOMMENDED VOLUME, INTENSITY, FREQUENCY, SET AND REP RANGE FOR HYPERTROPHY.
- Intensity: 60-85% of 1 rep max
- Volume: 3-6 sets per exercise / 6-12 repetitions per set
- Between reps: 30-90 seconds rest
- Frequency: 2 to 3 days per week of training has been effective in increasing musclehypertrophy. Higher frequencies may be used to fully maximize hypertrophy.
If you are doing weight training for the first time, the volume and intensity are kept low, the priority is to aim to do the exercises right.
HOW MANY DAYS A WEEK SHOULD I WORKOUT?
To get the expected results, it is important to train smart, but also to give your body a chance to recover properly. Proper recovery includes, among other things, a suitable diet and enough recovery time to give the body time to adapt to the muscular work to which it is subjected, as well as to improve your condition after each session.
FOR MUSCLE GAIN
Research findings support the notion that working muscle groups twice a week leads to more substantial gains in both muscle size and strength compared to training them only once a week. As a result, incorporating a minimum of two weekly sessions for the same muscle group could be a strategic approach to maximize your training outcomes.
For the same muscle group, 48 hours of recovery between sessions is usually sufficient. Remember that muscles are damaged during training and develop during rest. You can train 7 days a week, but you can’t work the same muscle group. For example; If you work the chest on Monday, the legs on Tuesday, and the shoulders on Wednesday, you will have enough rest time for the next chest workout.
BODYBUILDING: EXERCISE SELECTION
1. COMPOUND EXERCISES
Compound exercises involve multiple joint movements and engage several muscle groups simultaneously. These exercises are known for their efficiency in building overall strength and muscle mass. Compound exercises are highly recommended for beginners because they provide a strong foundation by developing functional strength and enhancing overall muscle coordination. They also burn more calories due to the involvement of multiple muscle groups.
Examples:
- Squats: Work the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, lower back, and core.
- Bench Press: Targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps.
- Deadlift: Engages the legs, lower back, upper back, and grip.
2. ISOLATION EXERCISES
Isolation exercises focus on a single muscle group, typically by moving only one joint. They are used to target specific muscles and enhance their size, shape, and definition.
Examples:
- Bicep Curl: Isolates the biceps.
- Tricep Pushdown: Targets the triceps.
- Dumbbell Fly: Focuses on the chest.
- Leg Curl: Isolates the hamstrings.
- Leg Extension: Targets the quadriceps.
For example, if you are designing a workout routine consisting of 3 exercises, you can do 2 exercises as compound and 1 exercise as isolation.
- Bench Press 3×10
- Incline Bench Press 3×10
- Dumbbell Fly 3×12
The truth is, they both have a time and a place, and we would recommend incorporating both into your workout plan to see maximum results.
THE FOUR ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS OF A GOOD WORKOUT PLAN ARE:
While there’s a wide variety of activities you could include in your workout plan, based on your own preference, goals and fitness level, there are four main types of physical activity to include in a well-rounded workout plan. You don’t necessarily have to do each of them each day, but they should each be incorporated regularly.
To make it easier on yourself to stick to a new training plan, there are a few important scheduling tips to follow:
“Cardio” exercise raises your heart rate and breathing to improve the function of your heart, lungs and circulatory system. Cardio can be a steady-state, low- to moderate-intensity exercise, or intervals of high intensity. It just needs to tax the large muscle groups strenuously enough and long enough to get you breathing heavily—which means you’re challenging your heart and lungs.
Cardio exercise doesn’t have to take place in a gym. Many activities in our daily lives can provide cardio exercise, like taking the stairs, raking leaves or shoveling snow. Aim for at least 2-3 cardio workouts per week—a 10-15-minute high-intensity workout or an hourlong low-intensity activity.
Example cardio activities: running, jogging, hiking, cycling, swimming, circuit training, HIIT, dancing, stair climbing, shoveling snow, raking leaves, playing sports like soccer, basketball, or hockey
Strength training helps build muscle, improve muscular strength and endurance, and is important in metabolism. It also helps to reduce injury from other activities and keep your skeletal system healthy as you age. Strength training exercises can be accomplished with simply your bodyweight, or can involve free weights, machines or resistance bands.
Flexibility & mobility First, a couple definitions: flexibility is the ability of a muscle to stretch and mobility is the ability of a joint to move freely through its range of motion. Both are important parts of overall fitness, and both should be incorporated into your fitness routine.
WARMING UP AND STRETCHING Warm-up helps prepare your body for aerobic activity. Because the main purpose of warming is to prepare your whole body for training. With a proper warm up exercise and stretching routine the elasticity and flexibility of the tendons and ligaments are increased. Warm-up and stretching is an activity that does not take much time, even a 5-10 minute warming routine will help you avoid injury.
Dynamic stretching consists of active movements. It is usually done before a workout to help warm up your muscles and increase your heart rate. Move slowly, stop and repeat, dig a little deeper each time and improve your range of motion. Pre-workout dynamic stretching improves circulation, prepares your muscles for movement, and temporarily increases your range of motion.
Static stretching, more commonly done at the end of a workout when your muscles are warm, is when stretches are held in place for a certain period of time, not moving. Static stretching is the most effective form of stretching for loosening up your muscles, joints, ligaments, and tendons, while also improving flexibility and range of motion. Static stretching requires you to move a muscle to the end of its range of motion and maintain this position for 20 to 45 seconds. Repeat this 2 to 3 times each.
Example flexibility & mobility activities: foam rolling, stretching, yoga, mobility exercises.
Recovery
How often do you aim to be active? Choose how many days per week you’d like to be active. While five days a week is certainly ideal, it’s also fine if you don’t want to have a formal workout schedule to follow each day of the week—maybe you’d like to choose four or five days per week of structured activities. Taking all of these factors into account, plan out a basic weekly workout schedule that works for you.
WHAT MUSCLE GROUPS SHOULD I WORK OUT TOGETHER?
The primary benefit of splitting different muscle groups onto different days is your ability to give each muscle more rest. Some muscle groups make good pairs to work out together. These are generally muscles or muscle groups that work with each other. A person can work these groups one day, then move onto another muscle group the next day.
However, everyone is different so which muscle groups to train together should be based on your personal outcomes and how you feel. For example, if you’re training on a weekly schedule and have one chest and arm day per week, your chest and arm have seven days to recover between sessions.
If you’re a beginner, sticking to those six basic muscle groups is enough to build a great workout routine that can help you improve your fitness.
BODYBUILDING TRAINING METHODS!
These training methods are high-intensity bodybuilding training techniques that rapidly increase muscle hypertrophy that will propel you further when your training routines become inefficient. The purpose of these sets is that you fatigue the target muscle group through a variety of rep and weight ranges, forcing your muscles to adapt and grow
PROGRESSIVE OVERLOAD
What is Progressive Overload; It is a working principle that involves gradually increasing the weight of your exercise over time so that you can continuously gain muscle, strength and endurance. It’s the gradual increase in strength by adding small weight plates every training session.
When you do intense weight training, your muscle fibers are subject to injury or stress. When your muscles are damaged in this way, satellite cells outside the muscle fibers come into play. The repair process involves rejoining the torn muscle fibers and introducing new proteins into each muscle cell. They try to repair the damage by bringing them together, as a result, they grow and strengthen the muscle fiber against this weight resistance.
DROP SETS
The drop set is a training method in which you perform an exercise until you fail, then immediately reduce the weight load. In particular, Drop sets; Maximizes the intensity of work sets as a method for increasing the time target muscles are under tension and metabolic stress. Increasing the duration of the muscle under tension means that the muscle growth is encouraged more.
Example Drop set:
Set 1: Start with a heavy weight for 6-8 reps
Ready, set drop…
Set 2: Drop the weight by 20-30 percent, do 10-12 reps
SUPERSETS
In weight training or other trainings, the principle of performing two exercises in a row without rest is called a superset. It emphasizes hypertrophy increase as well as endurance as it can be extremely difficult not to have rest between sets. Supersets are a effective working principle preferred to shock muscles. The benefits of supersets are quite metabolically efficient.
For Example:
You can pair two exercises that work the same muscle group or two exercises that pair opposing muscle groups.
- Chest Press and Chest Fly
- Bench Press and Barbell Bent Over
- Cable Curl and Pushdown
- Pec deck fly and Rear Delt Machine Fly
TRI-SETS
Just like supersets, but this time you will do three different exercises in a row without rest. Sounds hard, right?
For Example:
Shoulder Tri-sets
- 1×8 Military Press
- 1×10 Dumbbell Laterar Raise
- 1×8 Dumbbell Front Raise
Chest Tri-sets
- 1×8 Bench Press
- 1×10 Dumbbell Fly
- 1×8 Incline Dumbbell Press
GIANT SETS
Unlike a tri-set, a giant set involves performing at least 4 exercises back-to-back for the same body part with only ten seconds rest in between sets. Giant sets are a high-intensity training technique.
For Example:
- 1×8 Barbell Bent Over
- 1×8 Lat Pulldown
- 1×8 Sated Cable Row
- 1×8 Dumbbell Row
PYRAMID SET
In weight training, it is a periodic training applied by the method of decreasing the number of reps as the weight level increases or increasing the number of reps as the weight level decreases. Pyramid sets are a very popular method applied in bodybuilding programs to increase muscle mass. The reason training is so popular is because it yields significant results. That’s why it continues to be used by many professional bodybuilders.
For Example:
Reverse Pyramid:
- Set 1 – 50 lbs x 8 reps
- Set 2 – 40 lbs x 10 reps
- Set 3 – 30 lbs x 12 reps
Standart Pyramid:
- Set 1 – 30 lbs x 12 reps
- Set 2 – 40 lbs x 10 reps
- Set 3 – 50 lbs x 8 reps
In summary, bodybuilding for beginners involves understanding your body type, designing a customized workout program, selecting appropriate exercises, and considering factors like sets, reps, and rest periods. Beginners should focus on progressive overload and exercise selection, including compound and isolation exercises. A balanced workout plan should encompass strength training, cardiovascular exercise, flexibility, and core work. Sports nutrition plays a crucial role, with an emphasis on protein intake for muscle growth. Advanced training methods like drop sets, supersets, tri-sets, giant sets, and pyramid sets can be incorporated as you progress.